Tools1D
From SAXSutilities wiki
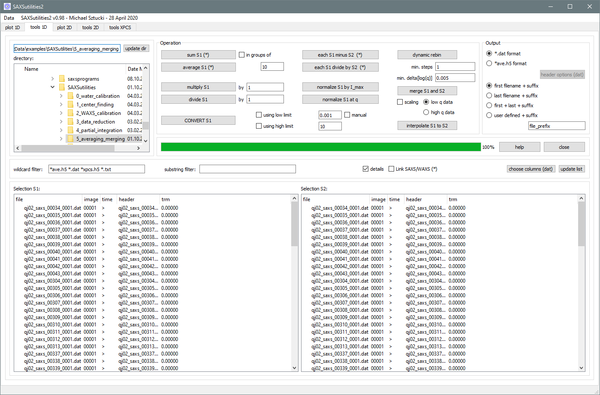
Graphical user interface for typical operations on one-dimensional files in ASCII (general) or HDF5 format (ID02: ending on _ave.h5 or _xpcs.h5) like summing, averaging, subtraction, merging, ... Routines for data conversion are available.
Contents
Features:
- Data sets with q vector, data and optionally error are supported. An appropriate error proagation is implemented for all available operations.
- Data are automatically interpolated to the q scale of the first file provided (if necessary).
- Combines SAXS/WAXS measurements can be now treated simultaneously. The same operation is executed for SAXS and WAXS files individually.
- History of performed operations is saved either in the first header line (ASCII) or and appropriate header key (HDF5).
- Output file name and data format can be chosen.
- A conversion between ASCII (*.dat) and HDF5 (*ave.h5) is available.
Specific features:
In the following a list of functions with more detailed description:
CONVERT
This allows to re-write all data sets selected in Selection S1.
- You can optionally restrict the q range of the created files at low and high q.
- By activating 'manual' you can choose the low q limit for each file separately by clicking on a graph. This is ideal for treating data which show unwanted artefacts at low q!
- The output data format can be chosen in the right top corner of the GUI. This is intended for converting data from ASCII to HDF5 and inverse.
SUM, AVERAGE, MINUS (each), DIVIDE (each)
- Summing and averaging can be done in groups of acertain number of images. The length of the selection must be a multiple of this number.
- All four functions can be combined with the option 'Link SAXS/WAXS'. In this case the operation is executed for two groups of files identified by _saxs_ and _waxs_ in the file name.
NORMALIZE
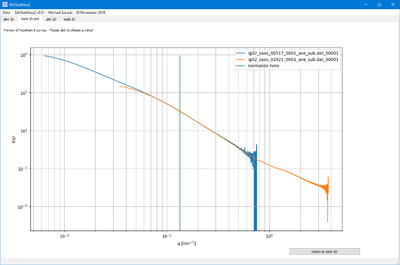
- This functions allow to either normalize the selected files by the maximum intensity or at a selected q value.
- In the second case, the q value is selected graphically. This allows to compare curves by scaling them in intensity.